Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Miwa, Kazuji; Takeda, Seiji; Iimoto, Takeshi*
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 184(3-4), p.372 - 375, 2019/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Environmental Sciences)The Ministry of the Environment has indicated the policy of recycling the contaminated soil generated by decontamination activity after the Fukushima accident. By recycling to coastal reclamation which is one of effective recycling application, dissolved radiocesium and absorbed radiocesium on soil particles will flow out to the ocean by construction, therefore evaluating radiocesium transition in ocean considering the both types of radiocesium is important for safety assessment. In this study, the radiocesium outflow during constructing and after constructing is modeled, and radiocesium transition in ocean is evaluated by Sediment model suggested in OECD/NEA. The adaptability of sediment model is confirmed by reproducing evaluation of the coastal area of Fukushima. We incorporate the sediment model to PASCLR2 code system to evaluate the doses from radiocesium in ocean.
Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Takizuka, Tomonori; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Fujita, Takaaki; Kamada, Yutaka; Ide, Shunsuke; Koide, Yoshihiko
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 48(5A), p.A55 - A61, 2006/05
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:24.63(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Matsumoto, Taro; Naito, Hiroshi*; Tokuda, Shinji; Kishimoto, Yasuaki
Physics of Plasmas, 12(9), p.092505_1 - 092505_7, 2005/09
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:6.85(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The behavior of the collisionless magnetohydrodynamics modes is investigated by the gyro-kinetic particle simulation in a cylindrical tokamak plasma in the parameter region where the effects of electron inertia and electron parallel compressibility are competitive for magnetic reconnection. Although the linear growth of the 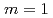 internal kink-tearing mode is dominated by the electron inertia, it is found that the growth rate can be nonlinearly accelerated due to the electron parallel compressibility proportional to the ion sound Larmor radius
internal kink-tearing mode is dominated by the electron inertia, it is found that the growth rate can be nonlinearly accelerated due to the electron parallel compressibility proportional to the ion sound Larmor radius 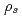 . It is also found that, as decreasing the electron skin depth
. It is also found that, as decreasing the electron skin depth 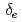 , the maximum growth rate before the internal collapse saturates independently of the microscopic scales such as
, the maximum growth rate before the internal collapse saturates independently of the microscopic scales such as 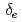 and
and 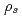 . The acceleration of growth rate is also observed in the nonlinear phase of the
. The acceleration of growth rate is also observed in the nonlinear phase of the 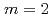 double tearing mode.
double tearing mode.
Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Takizuka, Tomonori; Ozeki, Takahisa
Nuclear Fusion, 45(8), p.933 - 941, 2005/08
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:41.32(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)We have investigated profile formation and sustainment of current hole (CH) plasma by 1.5D transport simulations with current limit model inside CH based on Axisymmetric Tri-Magnetic-Islands equilibrium. Sharp reduction of anomalous transport in RS region can reproduce JT-60U experiments. The transport becomes neoclassical-level in RS region, which results in autonomous profile formation of ITB and CH through large bootstrap current. ITB width determined by neoclassical-level transport agrees with that in JT-60U. Energy confinement inside ITB agrees with JT-60U scaling. The scaling means that core plasma inside ITB is governed by MHD equilibrium limit, i.e., autonomous limitation of energy confinement. The plasma with large CH is sustained with full current drive by bootstrap current. The plasma with small CH and small bootstrap current fraction shrinks due to penetration of inductive current. This shrink is prevented and CH size can be controlled by appropriate external CD. CH plasma is found to respond autonomically to external CD. Application of CH plasma to reactor is discussed.
Aiba, Nobuyuki*; Tokuda, Shinji; Ishizawa, Tomoko*; Okamoto, Masao*
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 46(11), p.1699 - 1721, 2004/11
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:9.95(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The theory of the Newcomb equation has been applied to low-n external modes in a tokamak and a method has been developed to compute the stability matrix that gives the change of plasma potential energy due to external modes in terms of the surface values of the perturbations. By using this method, the spectral properties of the ideal external modes has been elucidated, such as coupling between external modes and internal modes, and the difference of the stability properties between a normal shear tokamak and a reversed shear tokamak. These results will be also useful in the stability analysis of resistive wall modes.
Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Takizuka, Tomonori; Ozeki, Takahisa
Proceedings of 20th IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2004) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2004/11
Profile formation and sustainment of tokamak plasmas with current hole (CH) have been investigated by using 1.5D transport simulations. A current limit model inside CH based on the Axisymmetric Tri-Magnetic-Islands equilibrium is introduced. We found that the sharp reduction of anomalous transport in the reversed-shear (RS) region can reproduce JT-60U experiment. The transport becomes neoclassical-level in RS region, which results in the autonomous formation of internal transport barrier (ITB) and CH through large bootstrap current. ITB width determined by neoclassical-level transport agrees with that in JT-60U. Energy confinement inside ITB agrees with JT-60U scaling, which means autonomous limitation of energy confinement. The plasma with large CH is sustained with the full current drive by bootstrap current. The plasma with small CH and small bootstrap current fraction shrinks due to inductive current penetration. This shrink is prevented and the CH size can be controlled by appropriate external current drive (CD). The CH plasma is found to respond autonomically to external CD.
Kaneko, Tetsuji; Tsukatani, Ichiro; Kiuchi, Kiyoshi
JAERI-Tech 2004-035, 18 Pages, 2004/03
Fuel elements used in the Reduced-Moderation Water Reactor (RMWR) have the stacking structure consisting of MOX pellets and UO blankets in a fuel rod in order to attain the high breeding ratio and high burn-up simultaneously. It is a characteristic of the fuel elements that there is high thermal stress caused by inhomogeneous linear power density along the longitudinal direction of the fuel rod in comparison with the present LWR fuels. For this reason, it is important to estimate local deformation behavior of the fuel cladding tube with temperature difference caused by MOX pellet and UO
blankets in a fuel rod in order to attain the high breeding ratio and high burn-up simultaneously. It is a characteristic of the fuel elements that there is high thermal stress caused by inhomogeneous linear power density along the longitudinal direction of the fuel rod in comparison with the present LWR fuels. For this reason, it is important to estimate local deformation behavior of the fuel cladding tube with temperature difference caused by MOX pellet and UO blanket. The testing machine was designed to investigate thermal-fatigue behavior under biaxial stress condition. The testing machine consists of the temperature distribution control unit, low cycle fatigue testing unit and internal pressure loading unit, it is also possible to conduct the simulation tests to investigate effects of pressure change with burn-up and longitudinal load change due to operation modes and restriction of fuel rods.
blanket. The testing machine was designed to investigate thermal-fatigue behavior under biaxial stress condition. The testing machine consists of the temperature distribution control unit, low cycle fatigue testing unit and internal pressure loading unit, it is also possible to conduct the simulation tests to investigate effects of pressure change with burn-up and longitudinal load change due to operation modes and restriction of fuel rods.
Shelley, A.; Kugo, Teruhiko; Shimada, Shoichiro*; Okubo, Tsutomu; Iwamura, Takamichi
JAERI-Research 2004-002, 47 Pages, 2004/03
Neutronic study has been done for a PWR-type reduced-moderation water reactor with seed-blanket fuel assemblies to achieve a high conversion ratio, a negative void coefficient and a high burnup by using a MOX fuel. The results of the precise assembly burnup calculations show that the recommended numbers of seed and blanket layers are 15(S15) and 5(B5), respectively. By the optimization of axial configuration, the S15B5 assembly with the seed of 1000 2 mm high, internal blanket of 150 mm high and axial blanket of 400
2 mm high, internal blanket of 150 mm high and axial blanket of 400 2 mm high is recommended. In this configuration, the conversion ratio is 1.0 and the core average burnup is 38 GWd/t. The S15B5 assembly can attain the core average burnup of 45 GWd/t by decreasing the height of seed to 500
2 mm high is recommended. In this configuration, the conversion ratio is 1.0 and the core average burnup is 38 GWd/t. The S15B5 assembly can attain the core average burnup of 45 GWd/t by decreasing the height of seed to 500 2 mm, however, the conversion ratio becomes 0.97. The void and fuel temperature coefficients are negative for both of the configurations. Effect of metal or T-MOX (PuO
2 mm, however, the conversion ratio becomes 0.97. The void and fuel temperature coefficients are negative for both of the configurations. Effect of metal or T-MOX (PuO +ThO
+ThO ) fuel has been also investigated. Metal improves the conversion ratio but makes the void coefficient worse. T-MOX improves the void coefficient, but decreases the conversion ratio.
) fuel has been also investigated. Metal improves the conversion ratio but makes the void coefficient worse. T-MOX improves the void coefficient, but decreases the conversion ratio.
Endo, Akira; Sato, Kaoru; Noguchi, Hiroshi; Tanaka, Susumu; Iida, Takao*; Furuichi, Shinya*; Kanda, Yukio*; Oki, Yuichi*
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 256(2), p.231 - 237, 2003/05
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:45.77(Chemistry, Analytical)Size distributions of  Cl,
Cl, 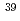 Cl,
Cl, 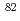 Br and
Br and 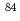 Br aerosols generated by irradiations of argon and krypton gases containing di-octyl phthalate (DOP) aerosols with 45MeV and 65MeV quasi-monoenergetic neutrons were measured to study the formation mechanism of radioactive particles in high energy radiation fields. Effects of the size distribution of the radioactive aerosols on the size of added DOP aerosols, the energy of irradiation neutrons and the kinds of nuclides were studied. The observed size distributions of the radioactive particles were explained by attachment of the radioactive atoms generated by the neutron-induced reactions to the DOP aerosols.
Br aerosols generated by irradiations of argon and krypton gases containing di-octyl phthalate (DOP) aerosols with 45MeV and 65MeV quasi-monoenergetic neutrons were measured to study the formation mechanism of radioactive particles in high energy radiation fields. Effects of the size distribution of the radioactive aerosols on the size of added DOP aerosols, the energy of irradiation neutrons and the kinds of nuclides were studied. The observed size distributions of the radioactive particles were explained by attachment of the radioactive atoms generated by the neutron-induced reactions to the DOP aerosols.
JT-60 Team
JAERI-Review 2002-022, 149 Pages, 2002/11
no abstracts in English
Wang, S.; Ozeki, Takahisa; Tobita, Kenji
Physical Review Letters, 88(10), p.105004_1 - 105004_4, 2002/03
Times Cited Count:130 Percentile:94.32(Physics, Multidisciplinary)A theoretical model has been established to show that energetic co-circulating ions can stabilize internal kink modes.And the theoretical model has been applied to interpret the recent experiments on sawtooth stabilization by energetic co-circulating ions.
Hatae, Takaki; JT-60 Team
Proceedings of 6th Japan-Australia Workshop on Plasma Diagnostics (CD-ROM), 13 Pages, 2002/00
The main purpose of JT-60U project is to make contribution to establishment of scientific basis of ITER and the demo tokamak reactor. Our ultimate goal is to achieve and sustain high integrated performance, namely high beta, high confinement, high bootstrap current fraction, full non-inductive current drive and heat/particle control, in a reactor-relevant regime. Toward this goal, we have developed weak magnetic shear ("high 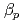 mode") and reversed magnetic shear plasmas. In both regimes, the internal transport barrier (ITB) and the edge pedestal are obtained simultaneously. As a large-sized tokamak equipped with a variety of devices for heating, current drive and profile control, JT-60U has high ability to approach the conditions required in reactors (ITER or demo): low values of normalized Larmor radius and collisionality, high toroidal field, high temperature with Te
mode") and reversed magnetic shear plasmas. In both regimes, the internal transport barrier (ITB) and the edge pedestal are obtained simultaneously. As a large-sized tokamak equipped with a variety of devices for heating, current drive and profile control, JT-60U has high ability to approach the conditions required in reactors (ITER or demo): low values of normalized Larmor radius and collisionality, high toroidal field, high temperature with Te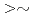 Ti, small central fueling, small ELM activities, etc. This paper reviews recent JT-60U results with the emphasis on the projection to the reactor-relevant regime.
Ti, small central fueling, small ELM activities, etc. This paper reviews recent JT-60U results with the emphasis on the projection to the reactor-relevant regime.
JT-60 Team
JAERI-Review 2000-035, 164 Pages, 2001/02
no abstracts in English
Matsumoto, Taro; Tokuda, Shinji; Kishimoto, Yasuaki; Takizuka, Tomonori; Naito, Hiroshi*
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 75(10), P. 1194, 1999/10
no abstracts in English
Matsumoto, Taro; Tokuda, Shinji; Kishimoto, Yasuaki; Takizuka, Tomonori; Naito, Hiroshi*
Journal of Plasma and Fusion Research SERIES, Vol.2, p.97 - 100, 1999/00
no abstracts in English
*; Yamagiwa, Mitsuru
Canadian Journal of Physics, 75(9), p.599 - 604, 1997/09
no abstracts in English
 Sn strands by internal tin diffusion prosess for the ITER project
Sn strands by internal tin diffusion prosess for the ITER project*; Kubo, Yoshio*; *; *; *; *; *; Isono, Takaaki; Nunoya, Yoshihiko; Yoshida, Kiyoshi; et al.
Teion Kogaku, 32(4), p.173 - 180, 1997/00
no abstracts in English
Tokuda, Shinji; Ozeki, Takahisa
JAERI-Research 94-030, 13 Pages, 1994/11
no abstracts in English
Ozeki, Takahisa; Azumi, Masafumi
JAERI-M 90-170, 23 Pages, 1990/10
no abstracts in English
Tsuji, Shunji; Azumi, Masafumi
Kaku Yugo Kenkyu, 61(5), p.287 - 306, 1989/05
no abstracts in English